
Dominance is not an autonomous feature
..of a gene or the product that it has information for. It depends as much on the gene product and the production of a particular phenotype from this product as it does on the particular phenotype that we choose to examine, in case more than one phenotype is influenced by the same gene.
Why are some alleles dominant and some recessive?
Every gene, contains the information to express a particular trait. In a diploid organism, two alleles need not always be identical, as in a heterozygote. One of them may be different due to some changes that it has undergone which modifies the information that particular allele contains.
Let’s take an example..
In heterozygous, Now there are two copies of gene, the two allelic forms. the normal allele (Unmodified allele) produces the normal enzyme that is needed for the transformation of a substrate S into product P
Theoretically, the modified allele could be responsible for production of – (i) the normal/less efficient enzyme, or (ii) a non-functional enzyme, or (iii) no enzyme at all
Unmodified Or Modified
-
Case-1-If The modified allele is equivalent to the unmodified allele
Result : It will produce the same phenotype/trait, i.e., result in the transformation of substrate S into P product. -
Case-2-If Modified Allele produces a non-functional enzyme or no enzyme
Result : The phenotype may be effected by different ways. Generally phenotype/trait will only be dependent on the functioning of the unmodified allele. -
Modified allele is generally the recessive allele.
Recessive trait in Population is due to non-functional enzyme or no enzyme is produced by modified allele.
Design for Understanding
-
100% Dominence
F1 resembled either of the two parents (i.e. Resemble with dominant) -
Incomplete-dominance
In this case, the F1 was in-between (both parents).RR x rr → Rr → Rr x Rr → 1:2:1 - Phenotype -
Co-dominance
In this case, the F1 generation resembles both parents.
Different types of red blood cells that determine ABO blood grouping in human beings is an Example of Codominence and..
Multiple Allelism
ABO Blood Group
The plasma membrane of the red blood cells has sugar polymers that protrude from its surface and the kind of sugar is controlled by the IA or IB gene.

ABO blood groups are controlled by the gene I
The gene (I) has three alleles IA , IB and i. The alleles IA and IB produce a slightly different form of the sugar while allele i does not produce any sugar.

Multiple Allelism
The gene (I) has three alleles IA , IB and i. The alleles IA and IB are Codominent over each other and Dominent over i. Since there are three different alleles, there are six different combinations of these three alleles that are possible, and therefore, a total of six different genotypes of the human ABO blood types
Multiple alleles
can be found only when Population studies are made.
Erythroblastosis fetalis
-
Rh positive
Red cells that are "Rh-positive" express the one designated D. About 15% of the population have no RhD antigen and thus are "Rh-negative".RhD incompatibility between mother and fetus.If the baby is Rh-positive (having inherited the trait from its father) and the mother Rh-negative.
-
The antibodies-IgG class
During birth, there is often a leakage of the baby's red blood cells into the mother's circulation. These red cells will cause her to develop antibodies against the RhD antigen.The antibodies, usually of the IgG class, do not cause any problems for that child, but can cross the placenta and attack the red cells of a subsequent Rh+ fetus.
-
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
This destroys the red cells producing anemia and jaundice. The disease, called erythroblastosis fetalis or hemolytic disease of the newborn, may be so severe as to kill the fetus or even the newborn infant. It is an example of an antibody-mediated cytotoxicity disorder. .
-
Summery
- Rh+ Male X Rh- Female
- First Child Not Affected
- IgG can cross the placenta
- Cure: Rh immune globulin (RhIG) or Rhogam
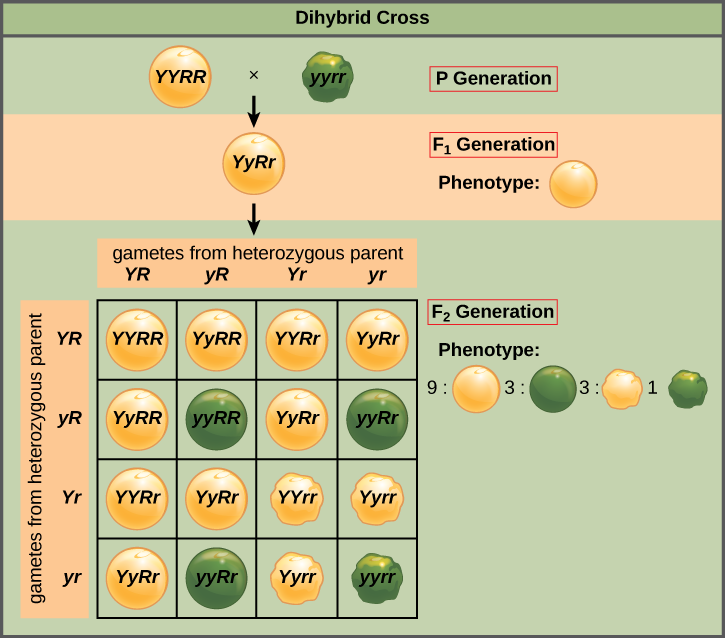
Mendel’s Law :
Independent Assortment
The law on the basis of dihybrid crosses, states that ‘when two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters’
- Phenotypic Ratio: 9:3:3:1
- Genotypic Ratio:1:1:1:1:4:2:2:2:2
- Law of Probability: The ratio of 9:3:3:1 can be derived as a combination series of 3 yellow: 1 green, with 3 round : 1 wrinkled.
Mendel published his work on inheritance of characters in 1865 but for several reasons, it remained unrecognised till 1900.
No Media Impact
Communication was not easy (as it is now) in those days and his work could not be widely publicised.
Factors as discrete units
was not accepted by his contemporaries as an explanation for the apparently continuous variation seen in nature..
Mathematics
to explain biological phenomena was totally new and unacceptable to many of the biologists of his time.
Physical proof
Mendel could not provide any physical proof for the existence of factors or say what they were made of.
More on Success and Failure.. ›

For NEET Biology Download
Our Apps : NEET Quickey and NEET PLay From Google Play.